Note
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try signing in or changing directories.
Access to this page requires authorization. You can try changing directories.
Applies to:
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Plan 1
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Plan 2
- Microsoft Defender XDR
Want to experience Defender for Endpoint? Sign up for a free trial.
If you're already completed the steps to prepare your environment for Defender for Endpoint, and you have assigned roles and permissions for Defender for Endpoint, your next step is to create a plan for onboarding. This plan should begin with identifying your architecture and choosing your deployment method.
We understand that every enterprise environment is unique, so we've provided several options to give you the flexibility in choosing how to deploy the service. Deciding how to onboard endpoints to the Defender for Endpoint service comes down to two important steps:
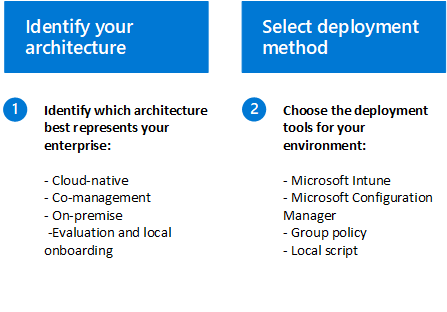
Step 1: Identify your architecture
Depending on your environment, some tools are better suited for certain architectures. Use the following table to decide which Defender for Endpoint architecture best suits your organization.
| Architecture | Description |
|---|---|
| Cloud-native | We recommend using Microsoft Intune to onboard, configure, and remediate endpoints from the cloud for enterprises who don't have an on-premises configuration management solution or are looking to reduce their on-premises infrastructure. |
| Co-management | For organizations who host both on-premises and cloud-based workloads we recommend using Microsoft's ConfigMgr and Intune for their management needs. These tools provide a comprehensive suite of cloud-powered management features, and unique co-management options to provision, deploy, manage, and secure endpoints and applications across an organization. |
| On-premises | For enterprises who want to take advantage of the cloud-based capabilities of Microsoft Defender for Endpoint while also maximizing their investments in Configuration Manager or Active Directory Domain Services, we recommend this architecture. |
| Evaluation and local onboarding | We recommend this architecture for SOCs (Security Operations Centers) who are looking to evaluate or run a Microsoft Defender for Endpoint pilot, but don't have existing management or deployment tools. This architecture can also be used to onboard devices in small environments without management infrastructure, such as a DMZ (Demilitarized Zone). |
Step 2: Select your deployment method
Once you have determined the architecture of your environment and have created an inventory as outlined in the requirements section, use the table below to select the appropriate deployment tools for the endpoints in your environment. This information will help you plan the deployment effectively.
| Endpoint | Deployment tool |
|---|---|
| Windows client devices | Microsoft Intune / Mobile Device Management (MDM) Microsoft Configuration Manager Local script (up to 10 devices) Group Policy Non-persistent virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) devices Azure Virtual Desktop System Center Endpoint Protection and Microsoft Monitoring Agent (for previous versions of Windows) |
| Windows Server (Requires a server plan) |
Local script Integration with Microsoft Defender for Cloud Guidance for Windows Server with SAP |
| macOS | Intune JAMF Pro Local script(manual deployment) MDM tools |
| Linux server (Requires a server plan) |
Installer script based deployment Ansible Chef Puppet Saltstack Manual deployment Direct onboarding with Defender for Cloud Guidance for Linux with SAP |
| Android | Microsoft Intune |
| iOS | Microsoft Intune Mobile Application Manager |
Note
For devices that aren't managed by Intune or Configuration Manager, you can use the Defender for Endpoint Security Settings Management to receive security configurations directly from Intune. To onboard servers to Defender for Endpoint, server licenses are required. You can choose from these options:
- Microsoft Defender for Servers Plan 1 or Plan 2 (as part of the Defender for Cloud) offering
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint for servers
- Microsoft Defender for Business servers (for small and medium-sized businesses only)
Next step
After choosing your Defender for Endpoint architecture and deployment method continue to Step 4 - Onboard devices.
Tip
Do you want to learn more? Engage with the Microsoft Security community in our Tech Community: Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Tech Community.